Alopecia areata is a complex autoimmune condition that affects millions worldwide, causing unpredictable hair loss patterns. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and most importantly, the various treatment options available to those affected. We’ll examine both traditional and cutting-edge therapies, discuss lifestyle modifications, and provide insights into managing the emotional aspects of living with alopecia areata.
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, impacting not just one’s appearance but also self-esteem and overall well-being. For individuals grappling with alopecia areata, understanding the condition and exploring available treatments is crucial. This article aims to empower readers with knowledge, offering hope and practical strategies for managing this challenging autoimmune disorder.
From corticosteroid injections to novel JAK inhibitors, we’ll explore the spectrum of medical interventions designed to stimulate hair regrowth and halt the progression of hair loss. Additionally, we’ll discuss complementary approaches, including dietary changes, stress management techniques, and innovative devices like the Hairegen system, which may offer additional support in the journey towards hair restoration.
Join us as we navigate the complexities of alopecia areata, uncovering the latest research, treatment modalities, and coping strategies. Whether you’re personally affected by this condition or seeking to support a loved one, this guide provides a comprehensive resource for understanding and addressing alopecia areata.
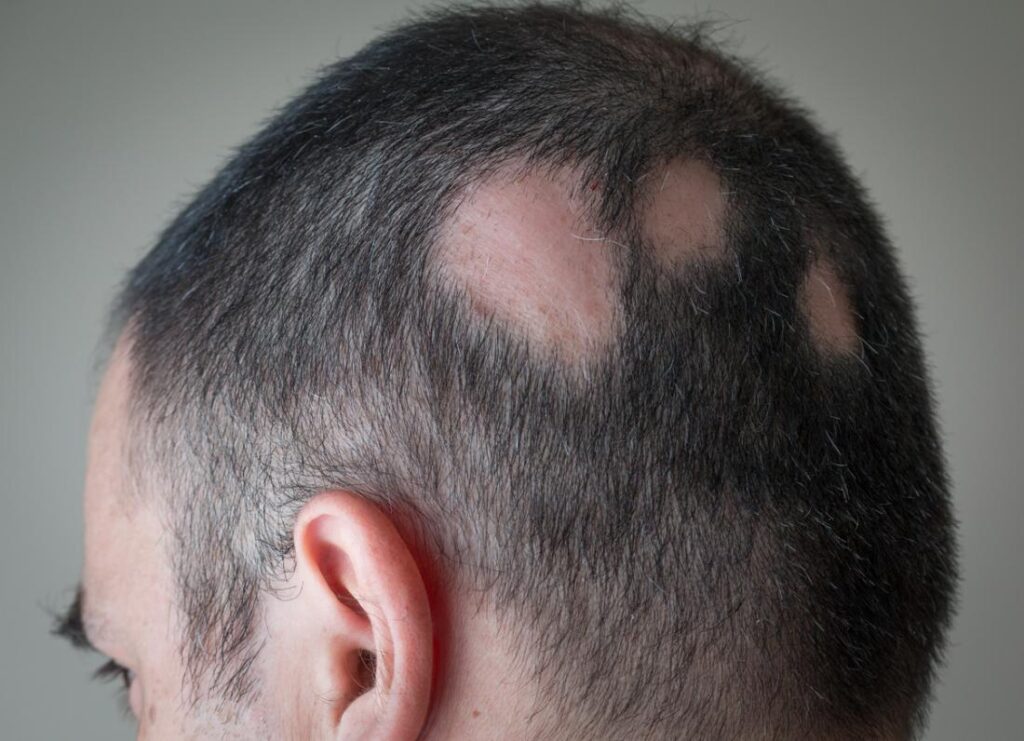
Understanding Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder characterized by sudden, patchy hair loss. This condition occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair shedding in various areas of the body. While it primarily affects the scalp, alopecia areata can impact any hair-bearing region, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and facial hair.
The exact mechanisms triggering this autoimmune response remain unclear, but researchers believe a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors play crucial roles. Individuals with a family history of autoimmune disorders or those experiencing high levels of stress may be at an increased risk of developing alopecia areata.
It’s important to note that alopecia areata is not contagious and does not pose direct health risks beyond hair loss. However, the psychological impact can be significant, affecting self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding the nature of this condition is the first step towards effective management and treatment.
Alopecia areata manifests in various forms, ranging from small, coin-sized patches of hair loss to more extensive balding. In some cases, individuals may experience complete hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or throughout the entire body (alopecia universalis). The unpredictable nature of hair loss and regrowth patterns adds to the challenges faced by those affected.
Despite its challenges, it’s crucial to remember that alopecia areata is a manageable condition. With advancements in medical research and a growing array of treatment options, many individuals find effective ways to stimulate hair regrowth and cope with the emotional aspects of hair loss.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Identifying the early signs of alopecia areata is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. The hallmark symptom is patchy hair loss, often appearing suddenly and without warning. These patches are typically smooth, round, and about the size of a coin, though they can vary in shape and size.
One distinctive feature of alopecia areata is the presence of “exclamation mark” hairs. These are short, broken hairs that taper at the bottom, resembling an exclamation point. They often appear around the edges of bald patches and can be a telltale sign of the condition.
While hair loss is the primary symptom, some individuals may experience additional signs:
- Itching or burning sensation in affected areas before hair loss occurs
- Changes in nail texture, including pitting or ridging of fingernails and toenails
- In some cases, widespread hair thinning rather than distinct patches
It’s important to note that alopecia areata can affect any hair-bearing area of the body. While the scalp is most commonly affected, hair loss can also occur in the beard, eyebrows, eyelashes, and even body hair. The extent and pattern of hair loss can vary greatly from person to person.
In some instances, individuals may notice white or gray hairs growing in areas previously affected by hair loss. This phenomenon, known as “overnight graying,” occurs when the condition preferentially affects pigmented hairs while sparing white ones.
The unpredictable nature of alopecia areata means that hair loss patterns can change over time. Some individuals may experience cycles of hair loss followed by regrowth, while others may have more persistent hair loss. Monitoring these changes and keeping track of symptoms can be helpful when discussing treatment options with healthcare providers.
It’s crucial to consult a dermatologist or trichologist if you suspect you may have alopecia areata. These specialists can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment strategies based on the specific manifestation of the condition.
Diagnosing Alopecia Areata
Accurate diagnosis of alopecia areata is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. Dermatologists and trichologists employ various methods to confirm the presence of this autoimmune condition and rule out other potential causes of hair loss.
The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough physical examination of the affected areas. A healthcare provider will closely inspect the scalp and other hair-bearing regions, looking for characteristic signs of alopecia areata such as smooth, round patches of hair loss and the presence of exclamation mark hairs.
In addition to the visual examination, doctors may use specialized tools to get a closer look at the scalp and hair follicles:
- Dermoscopy: This non-invasive technique uses a handheld device to magnify and illuminate the scalp, allowing for detailed observation of hair follicles and skin surface.
- Trichoscopy: A more advanced form of dermoscopy specifically designed for hair and scalp examination, providing high-resolution images for analysis.
To confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions, additional tests may be recommended:
Pull test: This simple procedure involves gently pulling on a small section of hair to assess the ease of hair removal and the number of hairs that come out.
Scalp biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of scalp tissue may be taken for microscopic examination. This can help confirm the diagnosis and provide information about the stage of the condition.
Blood tests: These may be ordered to check for other autoimmune disorders or nutritional deficiencies that could contribute to hair loss.
Genetic testing: While not routinely performed, genetic analysis can help identify specific genes associated with an increased risk of alopecia areata.
It’s important to provide your healthcare provider with a comprehensive medical history, including:
- Family history of alopecia areata or other autoimmune disorders
- Recent stressful events or lifestyle changes
- Any medications or supplements you’re taking
- Previous hair loss episodes and treatments tried
Accurate diagnosis is crucial not only for determining the most appropriate treatment approach but also for differentiating alopecia areata from other forms of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium. Each of these conditions requires different management strategies, making precise diagnosis essential for optimal outcomes.
Remember that alopecia areata can be a dynamic condition, with symptoms changing over time. Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider can help monitor the progression of the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Conventional Treatment Approaches
Once alopecia areata is diagnosed, healthcare providers can recommend a range of conventional treatments aimed at stimulating hair regrowth and halting further hair loss. These established therapies have shown varying degrees of success and are often the first line of defense against this autoimmune condition.
Topical Treatments
Topical medications are frequently prescribed as an initial treatment for alopecia areata, particularly for mild to moderate cases:
Corticosteroid creams and ointments: These anti-inflammatory agents can be applied directly to affected areas, reducing immune system activity in the hair follicles. They’re often used for small patches of hair loss.
Minoxidil: Originally developed as a blood pressure medication, minoxidil has shown efficacy in promoting hair growth. It’s available over-the-counter in various strengths and can be applied to the scalp twice daily.
Anthralin: This synthetic tar-like substance may help stimulate hair regrowth when applied for short periods and then washed off.
Topical immunotherapy: Chemicals like diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutyl ester (SADBE) are applied to the scalp to induce a mild allergic reaction, which may help stimulate hair growth.
Injectable Treatments
For more extensive hair loss or cases that don’t respond to topical treatments, injectable therapies may be recommended:
Intralesional corticosteroids: These involve injecting steroids directly into the bald patches. This targeted approach can be highly effective but may require repeated treatments.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): This innovative treatment uses a concentrated form of the patient’s own blood plasma, rich in growth factors, to stimulate hair follicles.
Systemic Medications
In cases of widespread or persistent alopecia areata, systemic treatments that affect the entire body may be prescribed:
Oral corticosteroids: These powerful anti-inflammatory drugs can suppress the immune system’s attack on hair follicles. However, they’re typically used for short periods due to potential side effects.
Immunosuppressants: Medications like methotrexate or cyclosporine may be prescribed to modulate the immune system’s response.
JAK inhibitors: A newer class of drugs, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, have shown promising results in clinical trials for treating severe alopecia areata.
Light Therapy
Phototherapy, particularly narrow-band UVB light treatment, has shown some efficacy in stimulating hair regrowth. This approach is often combined with other treatments for enhanced results.
Scalp Micropigmentation
While not a treatment for hair regrowth, scalp micropigmentation is a cosmetic procedure that can help camouflage hair loss by creating the appearance of a fuller head of hair through tattooing techniques.
It’s important to note that response to these conventional treatments can vary significantly among individuals. What works well for one person may not be as effective for another. Additionally, some treatments may need to be continued long-term to maintain results.
Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan, taking into account the extent of your hair loss, overall health, and personal preferences. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to the treatment regimen may be necessary to achieve optimal results in managing alopecia areata.

Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact the health of your hair and potentially slow the progression of female pattern baldness. These modifications, when combined with other treatments, can contribute to an overall strategy for managing hair loss.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss. Implementing stress-reduction techniques can be beneficial:
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Regular exercise
- Adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night)
- Yoga or tai chi
- Deep breathing exercises
- Engaging in hobbies and leisure activities
Gentle Hair Care Practices
Proper hair care can prevent unnecessary damage and breakage:
- Use a wide-toothed comb to detangle wet hair gently
- Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on the hair
- Limit use of heat styling tools
- Choose sulfate-free, gentle shampoos
- Use a silk or satin pillowcase to reduce friction
Scalp Care
A healthy scalp provides a better environment for hair growth:
- Regular scalp massages to improve blood circulation
- Use of scalp exfoliants to remove dead skin cells
- Maintaining proper scalp hygiene
- Protecting the scalp from sun damage with hats or SPF products
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise can improve overall health and potentially benefit hair growth:
- Cardiovascular exercises to improve blood circulation
- Strength training to support hormone balance
- Yoga poses that increase blood flow to the scalp
Avoiding Harmful Habits
Certain habits can contribute to hair damage and loss:
- Quit smoking, as it can damage hair follicles and affect circulation
- Limit alcohol consumption, which can lead to nutrient deficiencies
- Avoid crash diets, which can cause nutritional imbalances
Environmental Protection
Protecting your hair from environmental stressors can help maintain its health:
- Wear a hat or use UV-protective products when exposed to strong sunlight
- Use a swim cap in chlorinated pools
- Protect hair from harsh winds and extreme temperatures
Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep is crucial for overall health, including hair health:
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine
- Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool
Hormonal Balance
For women experiencing hormonal imbalances, working with a healthcare provider to address these issues can be beneficial:
- Regular check-ups to monitor hormone levels
- Discussing hormone replacement therapy options if appropriate
- Managing conditions like PCOS that can affect hair health
Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for hair and scalp health:
- Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily
- Include hydrating foods in your diet
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake, which can be dehydrating
By implementing these lifestyle modifications, women can create an environment that supports hair health and potentially slows the progression of female pattern baldness. It’s important to remember that these changes work best when combined with other treatments and should be part of a comprehensive approach to managing hair loss.
Natural and Herbal Remedies
Many women seek natural and herbal remedies as part of their approach to managing female pattern baldness. While scientific evidence for some of these treatments is limited, many have been used traditionally for hair health. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen.
Essential Oils
Certain essential oils are believed to promote hair growth and scalp health:
- Rosemary oil: May improve cellular generation and increase circulation
- Peppermint oil: Can stimulate the scalp and potentially promote hair growth
- Lavender oil: Known for its stress-reducing properties and potential to improve hair growth
- Tea tree oil: Has antimicrobial properties that can benefit scalp health
To use: Mix a few drops of essential oil with a carrier oil like coconut or jojoba oil. Massage into the scalp and leave for 30 minutes before washing.
Herbal Infusions
Herbal teas and infusions can be applied topically or consumed:
- Green tea: Rich in antioxidants that may promote hair growth
- Saw palmetto: May help block DHT, a hormone associated with hair loss
- Ginseng: Can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth
- Horsetail: Contains silica, which may strengthen hair
To use: Brew strong herbal teas and apply cooled to the scalp, or drink regularly as part of a healthy diet.
Ayurvedic Remedies
Ayurvedic medicine offers several treatments for hair health:
- Bhringraj oil: Traditionally used to prevent hair loss and premature graying
- Amla (Indian gooseberry): Rich in vitamin C and antioxidants
- Fenugreek seeds: Can nourish hair follicles and promote growth
To use: Apply Ayurvedic oils to the scalp or create masks using powdered herbs mixed with water or yogurt.
Scalp Treatments
Natural scalp treatments can improve overall scalp health:
- Aloe vera: Has moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties
- Onion juice: May improve circulation to hair follicles
- Apple cider vinegar: Can help balance scalp pH and remove buildup
To use: Apply these treatments directly to the scalp, leave for 15-30 minutes, then rinse thoroughly.
Dietary Supplements
Certain natural supplements may support hair health:
- Biotin: A B-vitamin that supports healthy hair growth
- Collagen: Can provide amino acids necessary for hair building
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Support overall hair health
- Zinc: Important for hair tissue growth and repair
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) approaches hair loss holistically:
- He Shou Wu: An herb believed to nourish the blood and benefit hair
- Goji berries: Rich in antioxidants and traditionally used for hair health
- Acupuncture: May improve blood flow to the scalp
Consult a licensed TCM practitioner for personalized treatment.
Natural Masks and Treatments
Homemade hair masks can nourish the scalp and hair:
- Egg mask: Rich in protein and nutrients
- Avocado and olive oil mask: Provides healthy fats and vitamins
- Coconut milk treatment: Can moisturize and nourish hair
To use: Apply masks to clean, damp hair, leave for 30 minutes, then rinse thoroughly.
While natural and herbal remedies can be a gentle way to support hair health, it’s important to remember that they may not be as potent as medical treatments for female pattern baldness. These remedies work best as part of a comprehensive approach that includes proper nutrition, stress management, and appropriate medical treatments when necessary. Always inform your healthcare provider about any natural remedies you’re using to ensure they don’t interact with other treatments or medications.
Best selling hair growth products:
Emerging Therapies and Research
The field of alopecia areata treatment is rapidly evolving, with researchers and pharmaceutical companies continually exploring new avenues for managing this challenging condition. These emerging therapies offer hope for individuals who may not have responded well to conventional treatments.
JAK Inhibitors: A Breakthrough in Treatment
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors have emerged as a promising class of medications for treating severe cases of alopecia areata. These drugs work by interrupting the signaling pathways that lead to the immune system’s attack on hair follicles. Several JAK inhibitors are currently in various stages of clinical trials and FDA approval:
- Baricitinib (Olumiant): Approved by the FDA in 2022 for treating severe alopecia areata in adults.
- Ritlecitinib: Showing promising results in clinical trials for both adults and adolescents with alopecia areata.
- Deuruxolitinib: Recently approved for treating adults with severe alopecia areata.
These medications represent a significant advancement in the treatment of alopecia areata, offering hope for those with extensive hair loss who have not responded to other therapies.
Stem Cell Therapy
Researchers are exploring the potential of stem cell therapy to regenerate hair follicles and promote hair growth. This approach involves:
- Harvesting stem cells from the patient’s own fat tissue or bone marrow
- Cultivating and processing these cells in a laboratory
- Injecting the processed cells into the scalp to stimulate hair follicle regeneration
While still in experimental stages, early results from small-scale studies have been encouraging, suggesting that stem cell therapy could become a viable treatment option in the future.
Gene Therapy
Advances in genetic research have opened up new possibilities for treating alopecia areata at its root cause. Scientists are investigating ways to:
- Identify specific genes associated with an increased risk of alopecia areata
- Develop targeted therapies that can modify or correct these genetic factors
- Potentially prevent the onset of alopecia areata in genetically predisposed individuals
Microbiome Modulation
Growing evidence suggests that the skin microbiome may play a role in the development and progression of alopecia areata. Researchers are exploring:
- Topical probiotics to promote a healthy scalp microbiome
- Targeted antimicrobial therapies to address imbalances in the skin microbiota
- Prebiotic treatments to support beneficial microorganisms on the scalp
Nanotechnology-Based Treatments
Nanotechnology offers exciting possibilities for delivering medications directly to hair follicles with greater precision and efficacy. Potential applications include:
- Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for enhanced absorption of topical treatments
- Nanoscale devices for targeted stimulation of hair follicles
- Nanofiber scaffolds to support hair follicle regeneration
Combination Therapies
Researchers are also investigating the potential of combining different treatment modalities to achieve synergistic effects. This approach may involve:
- Combining JAK inhibitors with traditional topical treatments
- Integrating light therapy with systemic medications
- Exploring multi-modal approaches that address both the immune system dysfunction and hair follicle regeneration
As research in these areas progresses, it’s likely that new treatment options will become available, offering hope for more effective management of alopecia areata across its various manifestations.
It’s important to note that many of these emerging therapies are still in experimental stages and may not be widely available. However, they represent the cutting edge of alopecia areata research and offer exciting possibilities for future treatment options.
Individuals interested in participating in clinical trials for new alopecia areata treatments can explore opportunities through resources like ClinicalTrials.gov or by discussing options with their healthcare providers.
Lifestyle and Complementary Approaches
While medical treatments play a crucial role in managing alopecia areata, lifestyle modifications and complementary approaches can significantly support overall hair health and potentially enhance the effectiveness of conventional therapies. These holistic strategies focus on creating an optimal environment for hair growth and addressing the broader impacts of the condition.
Nutritional Support
A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can promote hair health and support the body’s immune system:
- Protein: Hair is primarily composed of protein, making adequate intake crucial for hair growth. Include lean meats, fish, eggs, and plant-based protein sources in your diet.
- Iron: Iron deficiency can contribute to hair loss. Incorporate iron-rich foods like leafy greens, red meat, and legumes.
- Biotin: This B-vitamin is essential for hair health. Foods high in biotin include eggs, nuts, and sweet potatoes.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats support scalp health. Find them in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Vitamins A, C, and E: These antioxidants protect hair follicles from oxidative stress. Consume a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend nutritional supplements to address specific deficiencies.
Stress Management
Stress is believed to play a role in triggering or exacerbating alopecia areata. Implementing stress-reduction techniques can be beneficial:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Regular exercise
- Yoga or tai chi
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
Engaging in activities you enjoy and maintaining a strong support network can also help manage stress levels.
Scalp Care
Proper scalp care can create a healthy environment for hair growth:
- Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos to avoid irritating the scalp
- Avoid harsh chemical treatments and excessive heat styling
- Massage the scalp regularly to stimulate blood flow
- Consider using essential oils like lavender or rosemary, which may have hair-growth promoting properties (dilute with a carrier oil before applying)
Camouflage Techniques
While working on hair regrowth, various camouflage techniques can help boost confidence:
- Wigs and hairpieces: High-quality options are available in a range of styles and colors
- Scalp micropigmentation: A cosmetic procedure that creates the appearance of a fuller head of hair
- Eyebrow pencils and powders: For those experiencing eyebrow loss
- Scarves, hats, and headbands: Stylish accessories that can cover areas of hair loss
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find benefit in alternative therapies, although scientific evidence for their effectiveness in treating alopecia areata is limited:
- Acupuncture: May help reduce stress and improve overall well-being
- Aromatherapy: Certain essential oils are believed to promote hair growth when used in massage
- Herbal remedies: Some herbs like ginseng and saw palmetto are traditionally used for hair health
Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatments to ensure they don’t interfere with your primary treatment plan.
Support Groups and Counseling
The emotional impact of alopecia areata can be significant. Joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies:
- Connect with others who understand your experiences
- Learn practical tips for managing the condition
- Develop strategies for building self-esteem and confidence
Organizations like the National Alopecia Areata Foundation offer resources and support for individuals affected by the condition.
Sleep and Recovery
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and can support the body’s healing processes:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to promote better sleep
By incorporating these lifestyle and complementary approaches alongside medical treatments, individuals with alopecia areata can take a comprehensive approach to managing their condition. Remember that what works best can vary from person to person, so it may take some experimentation to find the right combination of strategies for your unique situation.
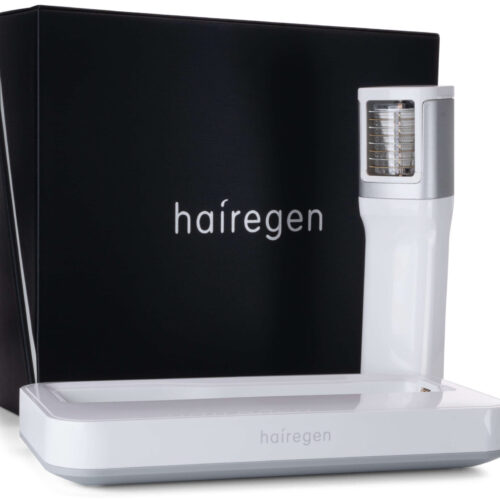
The Role of Hairegen Device in Alopecia Areata Treatment
In the landscape of alopecia areata treatment, innovative devices are emerging as potential complementary therapies. One such device gaining attention is the Hairegen system, which offers a non-invasive approach to stimulating hair growth in individuals affected by various forms of hair loss, including alopecia areata.
Understanding Hairegen Technology
The Hairegen device utilizes low-level laser therapy (LLLT) to promote hair growth. This technology works by:
- Emitting specific wavelengths of light that penetrate the scalp
- Stimulating cellular activity in hair follicles
- Increasing blood flow to the scalp
- Potentially reducing inflammation associated with alopecia areata
Potential Benefits for Alopecia Areata Patients
While research on the specific efficacy of Hairegen for alopecia areata is ongoing, LLLT has shown promising results in various hair loss conditions:
- Increased hair density and thickness
- Improved hair growth rate
- Enhanced overall hair quality
For individuals with alopecia areata, Hairegen may offer several advantages:
- Non-invasive treatment option
- Minimal side effects compared to some medications
- Can be used in conjunction with other treatments
- Convenient for at-home use
Using Hairegen as Part of a Comprehensive Treatment Plan
Incorporating Hairegen into an alopecia areata treatment regimen typically involves:
- Consulting with a healthcare provider to determine if LLLT is appropriate for your specific case
- Following a prescribed treatment schedule, usually involving regular sessions several times per week
- Combining Hairegen use with other recommended treatments and lifestyle modifications
- Monitoring progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed
It’s important to note that while Hairegen and similar LLLT devices show promise, they are generally considered complementary therapies. They work best when used as part of a comprehensive treatment approach under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
As with any treatment for alopecia areata, individual results may vary, and patience is key. Consistent use over several months may be necessary before noticeable improvements are observed.

Managing the Emotional Impact
Living with alopecia areata can be emotionally challenging, affecting self-esteem, body image, and overall quality of life. Addressing the psychological aspects of this condition is just as crucial as treating the physical symptoms. Here are strategies to help manage the emotional impact of alopecia areata:
Acknowledging Your Feelings
It’s normal to experience a range of emotions when dealing with hair loss:
- Grief over the loss of hair and changes in appearance
- Anxiety about future hair loss or social situations
- Frustration with the unpredictable nature of the condition
- Anger or sadness about the impact on daily life
Recognizing and accepting these feelings is an important step in the coping process. Remember that your emotions are valid, and it’s okay to take time to process them.
Seeking Professional Support
Mental health professionals can provide valuable support in navigating the emotional challenges of alopecia areata:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps identify and change negative thought patterns related to hair loss
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Focuses on accepting difficult experiences and committing to actions aligned with personal values
- Support groups: Offer a safe space to share experiences and coping strategies with others facing similar challenges
Don’t hesitate to reach out to a therapist or counselor specializing in chronic health conditions or body image issues.
Building a Support Network
Surrounding yourself with understanding and supportive individuals can make a significant difference:
- Share your experiences with trusted friends and family members
- Connect with others who have alopecia areata through support groups or online communities
- Educate your social circle about the condition to foster understanding and empathy
Developing Coping Strategies
Practical coping mechanisms can help you navigate daily challenges:
- Practice positive self-talk and affirmations
- Focus on your strengths and qualities beyond physical appearance
- Engage in activities that boost your confidence and self-esteem
- Explore creative expression through art, writing, or music as an outlet for emotions
Embracing Your Unique Appearance
While it’s natural to want to conceal hair loss, some individuals find empowerment in embracing their appearance:
- Experiment with different looks, including going completely bald
- Use head coverings as a form of self-expression with various colors and styles
- Consider temporary or permanent scalp tattoos as a way to reclaim your appearance
Educating Others
Raising awareness about alopecia areata can help reduce stigma and misconceptions:
- Share information about the condition with friends, family, and colleagues
- Participate in awareness campaigns or fundraising events
- Consider becoming an advocate for alopecia areata research and support
Practicing Self-Care
Prioritizing self-care is essential for managing stress and maintaining overall well-being:
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing
- Maintain a balanced diet and ensure adequate sleep
- Pursue hobbies and interests that bring joy and fulfillment
Setting Realistic Expectations
Understanding that alopecia areata is a chronic condition with unpredictable patterns can help manage expectations:
- Focus on progress rather than perfection in treatment outcomes
- Celebrate small victories in hair regrowth or emotional resilience
- Be patient with the treatment process, as results may take time to manifest
Exploring Body Image Workshops
Some organizations offer workshops specifically designed to address body image concerns related to hair loss:
- Learn techniques for improving body acceptance
- Develop strategies for handling social situations confidently
- Connect with others facing similar challenges in a supportive environment
Remember that managing the emotional impact of alopecia areata is an ongoing process. It’s okay to have good days and bad days. The key is to develop a toolkit of coping strategies and support systems that you can rely on throughout your journey.
By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of alopecia areata, individuals can work towards not just managing the condition, but thriving despite its challenges. With the right support and mindset, it’s possible to cultivate resilience, self-acceptance, and a positive outlook on life beyond hair loss.
Future Directions in Alopecia Areata Research
The field of alopecia areata research is dynamic and rapidly evolving, with scientists and medical professionals continually striving to deepen our understanding of the condition and develop more effective treatments. As we look to the future, several promising areas of research offer hope for improved management and potential breakthroughs in treating this challenging autoimmune disorder.
Genetic Studies and Personalized Medicine
Advancements in genetic research are paving the way for more targeted treatments:
- Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are identifying specific genetic markers associated with alopecia areata susceptibility
- Researchers are exploring how genetic variations influence treatment responses, potentially leading to personalized treatment plans
- Gene therapy approaches are being investigated as a means of correcting genetic factors contributing to the condition
These genetic insights may eventually allow for early intervention in high-risk individuals and more precise treatment selection based on an individual’s genetic profile.
Immunology and Targeted Therapies
As our understanding of the immune mechanisms underlying alopecia areata deepens, new therapeutic targets are emerging:
- Research into T-cell signaling pathways is uncovering potential new drug targets
- Studies on regulatory T-cells (Tregs) are exploring ways to modulate the immune response more effectively
- Investigations into cytokine networks may lead to more targeted immunotherapies
These advancements could result in treatments that more precisely address the autoimmune dysfunction in alopecia areata while minimizing side effects.
Microbiome Research
The role of the skin and gut microbiome in autoimmune conditions is an area of growing interest:
- Scientists are investigating how the scalp microbiome differs in individuals with alopecia areata
- Research is exploring the potential of probiotic and prebiotic treatments to modulate the microbiome and influence immune function
- Studies are examining the gut-skin axis and its potential impact on alopecia areata development and progression
Understanding the microbiome’s role could lead to novel treatment approaches that focus on restoring microbial balance.
Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Therapies
Advances in regenerative medicine offer exciting possibilities for hair follicle regeneration:
- Research into hair follicle stem cells is exploring ways to activate dormant follicles
- Tissue engineering techniques are being developed to create new hair follicles
- Studies on exosomes and growth factors are investigating their potential to stimulate hair growth
These approaches could potentially offer solutions for even the most severe cases of alopecia areata.
Nanotechnology and Drug Delivery
Innovations in nanotechnology are opening up new avenues for targeted drug delivery:
- Nanoparticle-based delivery systems are being developed to enhance the efficacy of topical treatments
- Research into nano-scale devices for follicle stimulation is ongoing
- Scientists are exploring the use of nanofibers as scaffolds for hair follicle regeneration
These advancements could lead to more effective and less invasive treatment options.
Artificial Intelligence and Big Data
The integration of AI and big data analytics is revolutionizing alopecia areata research:
- Machine learning algorithms are being used to analyze large datasets and identify patterns in disease progression and treatment responses
- AI-powered imaging technologies are improving diagnosis and monitoring of hair loss
- Predictive models are being developed to forecast treatment outcomes and guide clinical decision-making
These tools have the potential to accelerate research and improve patient care by providing more personalized and data-driven treatment approaches.
Clinical Trial Innovations
The landscape of clinical trials for alopecia areata treatments is evolving:
- Adaptive trial designs are allowing for more efficient testing of multiple treatments
- Patient-reported outcomes are being given greater emphasis in assessing treatment efficacy
- Virtual and decentralized trials are making participation more accessible to a broader range of patients
These innovations could lead to faster development and approval of new treatments.
Psychosocial Research
Recognizing the significant emotional impact of alopecia areata, researchers are also focusing on psychosocial aspects:
- Studies are exploring the effectiveness of various psychological interventions in improving quality of life for those with alopecia areata
- Research is investigating the long-term psychological outcomes of different treatment approaches
- Work is being done to develop and validate tools for assessing the psychosocial burden of the condition
This research aims to provide a more holistic approach to alopecia areata management, addressing both physical and emotional well-being.
As these various research directions progress, the future of alopecia areata treatment looks increasingly promising. While a cure remains elusive, the potential for more effective, personalized, and comprehensive management strategies is on the horizon.
It’s important for individuals affected by alopecia areata to stay informed about these developments and discuss emerging treatment options with their healthcare providers. Participation in clinical trials, when appropriate, can also contribute to the advancement of research and potentially provide access to cutting-edge treatments.
The ongoing dedication of researchers, clinicians, and patients in the field of alopecia areata offers hope for continued improvements in our understanding and treatment of this challenging condition. As we look to the future, the combined efforts of the scientific community and those living with alopecia areata promise to drive meaningful progress in managing this autoimmune disorder.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata presents unique challenges, but with ongoing research and a multifaceted approach to treatment, individuals affected by this condition have more options than ever before. From conventional therapies to emerging treatments and lifestyle modifications, the landscape of alopecia areata management continues to evolve.
Key takeaways from this comprehensive guide include:
- Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
- A personalized treatment plan, often combining multiple approaches, is crucial for managing alopecia areata effectively.
- Emerging therapies, such as JAK inhibitors and regenerative medicine, offer new hope for those with severe or treatment-resistant cases.
- Lifestyle factors, including nutrition, stress management, and scalp care, play important roles in supporting overall hair health.
- Addressing the emotional impact of alopecia areata is just as important as treating the physical symptoms.
- Staying informed about research developments and participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments.
As we look to the future, the field of alopecia areata research continues to advance, promising more targeted and effective treatments. The integration of genetic insights, immunological research, and innovative technologies like the Hairegen device offers hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Remember that managing alopecia areata is a journey, and what works best can vary from person to person. Patience, persistence, and open communication with healthcare providers are key to finding the most effective treatment approach for each individual.
By combining medical treatments with lifestyle modifications, emotional support, and a proactive approach to self-care, individuals with alopecia areata can work towards not just managing their condition, but thriving despite its challenges. With ongoing research and a supportive community, the future holds promise for better understanding and more effective management of alopecia areata.