Hair loss is a prevalent concern that affects individuals across various demographics, including age, gender, and ethnicity. While many factors contribute to this condition, such as genetics, hormonal changes, and stress, nutritional deficiencies—particularly vitamin deficiencies—play a crucial role. This article delves into the specific vitamins whose lack can lead to hair loss, providing insights into their functions, symptoms of deficiency, and how to address these issues effectively.

The Importance of Vitamins in Hair Health
Vitamins are essential organic compounds that our bodies require in small amounts to function optimally. They play a significant role in numerous bodily processes, including cellular growth and repair, immune function, and metabolism. When it comes to hair health, specific vitamins are particularly vital, as they contribute to the growth cycle of hair follicles, enhance the strength of hair strands, and protect against oxidative stress.
Key Vitamins for Hair Growth
Several vitamins have been identified as crucial for maintaining healthy hair. These include:
- Vitamin A: Essential for cell growth and differentiation, vitamin A helps produce sebum, an oil that keeps hair moisturized.
- B Vitamins: This group includes several essential vitamins, such as B12, B7 (biotin), and B9 (folate), which are integral to energy production and the formation of red blood cells.
- Vitamin C: Known for its antioxidant properties, vitamin C protects hair follicles from oxidative damage and aids in collagen production, vital for hair structure.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin promotes the creation of new hair follicles, essential for hair growth.
- Vitamin E: With its antioxidant properties, vitamin E helps reduce oxidative stress and supports a healthy scalp.
Understanding which vitamin deficiency causes hair loss is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.
How Vitamin Deficiencies Lead to Hair Loss
When the body lacks essential vitamins, it can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to various forms of hair loss. The relationship between vitamin deficiencies and hair health is complex; deficiencies can affect the hair growth phase, leading to thinning, brittleness, and excessive shedding.
The Hair Growth Cycle
To comprehend how vitamin deficiencies impact hair loss, it’s essential to understand the hair growth cycle, which consists of three main phases:
- Anagen Phase: The active growth phase where hair follicles produce new hair.
- Catagen Phase: A transitional phase where hair growth slows, and follicles shrink.
- Telogen Phase: The resting phase before hair falls out and new hair begins to grow.
A deficiency in vital vitamins can shorten the anagen phase, leading to premature hair shedding and reduced hair density.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining healthy hair follicles. It plays a role in the creation of keratinocytes, the cells that form hair follicles. Low levels of vitamin D can lead to hair loss due to insufficient keratinocyte production.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Dry, brittle hair: Hair may become more prone to breakage.
- Increased shedding: Noticeable hair loss during washing or styling.
- Thinning hair: A general reduction in hair density.
Sources and Treatment for Vitamin D
To combat vitamin D deficiency, consider:
- Sun Exposure: Regularly spending time outdoors can help boost vitamin D levels.
- Diet: Incorporate vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products.
- Supplements: Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate supplementation.
Vitamin B12 and Hair Loss
Vitamin B12 is essential for DNA synthesis and red blood cell production. A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to hair loss due to impaired hair follicle function.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Excessive hair shedding: Increased loss of hair strands during daily grooming.
- Slow hair regrowth: Difficulty in regrowing hair after shedding.
- Fatigue and weakness: Generalized tiredness that may accompany hair loss.
Sources and Treatment for Vitamin B12
To increase your vitamin B12 intake, consider:
- Animal Products: Foods like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy are rich in B12.
- Fortified Foods: Some cereals and plant-based milk are fortified with B12.
- Supplements: B12 supplements are available, especially for those following a vegan or vegetarian diet.

Iron Deficiency and Its Impact on Hair
Iron is critical for transporting oxygen to hair follicles, which is essential for healthy hair growth. A deficiency can lead to iron deficiency anemia, a common cause of hair loss.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency
- Increased hair shedding: Noticeable loss of hair strands during washing or brushing.
- Brittle hair: Hair may become weak and prone to breakage.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness due to low iron levels.
Sources and Treatment for Iron
To address iron deficiency, focus on:
- Iron-Rich Foods: Include red meat, poultry, fish, lentils, and spinach in your diet.
- Cooking with Cast Iron: This can help increase iron content in food.
- Supplements: Consult a healthcare provider for iron supplementation if necessary.
The Role of Vitamin A in Hair Health
Vitamin A is vital for cell growth and the production of sebum, which keeps hair moisturized. A deficiency can lead to dry, brittle hair and increased shedding.
Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency
- Dry hair and scalp: Lack of moisture can lead to hair breakage.
- Dandruff: Flaky scalp conditions may arise from insufficient sebum production.
- Slow hair growth: Reduced hair growth rates may be observed.
Sources and Treatment for Vitamin A
To ensure adequate vitamin A levels, consider:
- Diet: Incorporate foods rich in beta-carotene, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
- Supplements: Use vitamin A supplements cautiously, as excessive intake can be harmful.
Vitamin E and Its Protective Effects
Vitamin E is known for its antioxidant properties, protecting hair follicles from oxidative stress. A deficiency can lead to increased hair shedding and poor scalp health.
Symptoms of Vitamin E Deficiency
- Increased hair loss: Noticeable shedding, especially when styling.
- Dry, damaged hair: Hair may become more prone to breakage.
- Scalp issues: A dry or irritated scalp can occur.
Sources and Treatment for Vitamin E
To boost vitamin E levels, focus on:
- Diet: Include nuts, seeds, spinach, and avocados in your meals.
- Topical Applications: Natural oils containing vitamin E can be applied to the scalp and hair.
Folic Acid: A B Vitamin Essential for Hair Growth
Folic acid, or vitamin B9, is crucial for cell division and growth. A deficiency can impair hair follicle function, leading to increased hair loss.
Symptoms of Folic Acid Deficiency
- Slowed hair growth: Reduced rate of new hair production.
- Thinning hair: Noticeable decrease in hair volume.
- Brittle hair: Increased breakage and damage.
Sources and Treatment for Folic Acid
To enhance folic acid intake, consider:
- Leafy Greens: Foods like spinach, kale, and broccoli are excellent sources.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils are rich in folate.
- Supplements: Folic acid supplements can be beneficial, especially for pregnant women.
Best selling hair growth products:
The Impact of Biotin Deficiency on Hair
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is essential for the metabolism of fats and amino acids, which are crucial for hair structure. A deficiency can lead to hair thinning and loss.
Symptoms of Biotin Deficiency
- Hair thinning: Noticeable reduction in hair density.
- Brittle hair: Increased fragility and breakage.
- Skin issues: Rashes or dermatitis may accompany hair loss.
Sources and Treatment for Biotin
To increase biotin levels, focus on:
- Diet: Include whole grains, eggs, nuts, and seeds in your meals.
- Supplements: Biotin supplements are widely available and may help those with deficiencies.
The Importance of Zinc for Hair Health
Zinc is a vital mineral that supports hair tissue growth and repair. It plays a role in maintaining the oil glands around hair follicles. A deficiency can lead to hair loss and scalp issues.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Increased hair shedding: Noticeable loss during grooming.
- Slow healing: Scalp wounds may take longer to heal.
- Dull hair: Lack of shine and vitality in hair strands.
Sources and Treatment for Zinc
To enhance zinc intake, consider:
- Diet: Include oysters, meat, beans, and nuts in your meals.
- Supplements: Zinc supplements can be recommended, especially for those with dietary restrictions.
Recognizing Symptoms of Vitamin Deficiencies
Understanding the symptoms associated with vitamin deficiencies is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Common signs include:
- Hair Shedding: Noticeable loss of hair during daily activities.
- Brittle Strands: Hair that breaks easily or appears dull.
- Scalp Issues: Flaky or irritated scalp conditions.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you experience significant hair loss or related symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider or a dermatologist is essential. They can perform blood tests to determine vitamin levels and recommend appropriate treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss Due to Vitamin Deficiencies
Addressing hair loss caused by vitamin deficiencies typically involves a combination of dietary changes, supplementation, and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some strategies:
Dietary Adjustments
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, emphasizing whole foods.
- Meal Planning: Incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods to ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins.
Supplements
- Consultation: Work with a healthcare provider to determine the right supplements based on individual deficiencies.
- Regular Monitoring: Periodically check vitamin levels to ensure they are within a healthy range.
Lifestyle Changes
- Stress Management: Implement stress-reducing practices such as meditation, yoga, or exercise.
- Avoiding Harmful Practices: Limit the use of heat styling tools and harsh chemical treatments.
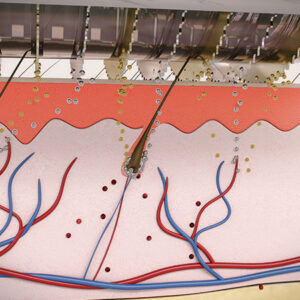
The Hairegen Device: A New Approach to Hair Restoration
In addition to dietary and lifestyle interventions, advanced technologies like the Hairegen device have emerged as promising options for addressing hair loss. This device utilizes low-level laser therapy (LLLT) to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
How the Hairegen Device Works
- Laser Technology: The device emits low-level lasers that penetrate the scalp, enhancing blood circulation and encouraging hair follicle activity.
- Non-Invasive Treatment: This approach is painless and can be easily integrated into a daily routine.
Benefits of Using the Hairegen Device
- Enhanced Hair Growth: Users may experience an increase in hair density and thickness.
- Safe and Effective: The device is designed for home use, offering a convenient solution for those dealing with hair loss.
Conclusion
Understanding which vitamin deficiency causes hair loss is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. By ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals, individuals can support their hair health and mitigate the risk of hair loss. If you suspect a deficiency, consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options. With the right approach, it is possible to restore hair vitality and achieve healthier, fuller hair.
Best selling hair growth products: