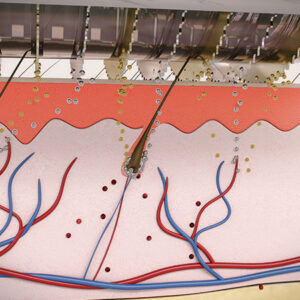
Hair on your pillow or in the shower drain can trigger immediate worry. Studies show that over 50% of men and women will experience noticeable hair loss by age 50. This makes it one of the most common health concerns worldwide.
Hair loss might feel isolating, but knowing why it happens helps you deal with it better. Male pattern baldness often gets the spotlight. Women’s hair loss is equally common, though it shows up differently.
This detailed guide covers the top 5 hair loss causes affecting both men and women. You’ll understand the science behind hair loss and spot early warning signs. The guide also reveals proven strategies that can help keep your hair healthy.

Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
Hair loss makes more sense when you learn how your hair naturally grows and sheds. Your scalp has about 100,000 hairs, and each follows its own growth cycle.
The Three Phases of Hair Growth
Your hair cycles through three distinct growth phases:
The Anagen Phase (Growth): Your hair grows actively during this period that lasts 2-7 years. Hair grows about one-fourth to one-half inch each month.
The Catagen Phase (Transition): This quick transition lasts about 2-4 weeks. Your hair follicle gets smaller and separates from the dermal papilla.
The Telogen Phase (Resting): The final phase continues for 2-4 months. About 10-15% of your scalp hair rests in this phase at any time.
Normal vs. Abnormal Hair Loss
You might feel less worried about hair loss once you know what’s normal. Losing 50-100 hairs each day is natural. Your hair renews itself through this regular shedding.
But your hair loss might need attention if you see:
- More than 100-150 hairs falling daily
- A sudden spike in daily shedding
- Specific areas getting thinner
- Your hair’s growth pattern changing
Signs Your Hair Loss Needs Medical Attention
These signs mean you should talk to a healthcare provider:
Sudden or Rapid Loss: Large clumps of hair falling out during shampooing or brushing.
Pattern Changes: Look out for unusual hair loss patterns, especially:
- Hair loss starting early (teens or twenties)
- Patchy or circular bald spots
- Your scalp showing redness, scaling, or other unusual changes
Additional Symptoms: Watch for hair loss combined with:
- Weight changes without explanation
- Feeling tired or sensitive to cold
- Unusual facial hair growth
- Irregular menstrual cycles
Early treatment often helps manage hair loss better. Some daily hair shedding is normal, but major changes in your hair’s growth cycle or unusual loss patterns need a doctor’s evaluation.
Genetic Factors in Hair Loss
Your hair loss might worry you if your parents or grandparents lost substantial amounts of hair. Genetics determines about 80% of your likelihood to experience baldness.
Male Pattern Baldness Genetics
Male pattern baldness has a more complex genetic blueprint than previously believed. Many people believe baldness comes from their mother’s side. However, research shows both parents contribute to hair loss risk. Men whose fathers experienced baldness face 5-6 times higher chances of developing it themselves.
Multiple genes create this inheritance pattern, and the androgen receptor (AR) gene takes center stage. Your hair follicles respond to hormones, especially DHT, because of this gene. Scientists discovered AR gene variations in 98.1% of young bald men and 92.3% of older bald men.
Female Pattern Hair Loss Inheritance
Women face their own unique genetic story. Family history substantially increases your risk of hair loss as a woman, especially from your mother’s side. Studies reveal that 62.2% of women with pattern hair loss have relatives with the same condition.
Key Inheritance Patterns in Women:
- Multiple affected family members increase prevalence
- Hair loss appears three times more often before age 40 with affected grandparents
- Maternal side inheritance shows stronger links
When to Expect Hereditary Hair Loss
Your genetic makeup substantially influences when hereditary hair loss begins. Research reveals these onset patterns:
For Men:
- Signs can appear after puberty
- Half of Caucasian men show signs by age 50
- Numbers rise to about 80% by age 70
For Women:
- Signs emerge in your 20s or 30s
- Risk rises substantially after menopause
- Strong genetic influence often shows before age 40
Genetics affects both your likelihood of hair loss and your response to treatment. Your family history helps healthcare providers create a more effective plan to manage potential hair loss.

Hormonal Imbalances and Hair Loss
Hormonal changes can substantially affect your hair’s growth cycle and cause different types of hair loss. You can identify and fix the root cause of hair loss by learning how hormones affect your hair.
Thyroid Disorders Impact on Hair
Thyroid hormones are vital in regulating hair growth and maintenance. A malfunctioning thyroid disrupts your hair’s natural cycle. Studies show that hair loss affects about 50% of people with hyperthyroidism and 33% with those who have hypothyroidism.
A thyroid condition might cause:
- Diffuse thinning across your scalp
- Changes in hair texture and strength
- Loss of hair in other body areas
- Delayed hair regrowth
Pregnancy and Postpartum Hair Loss
Your hair becomes thicker and more vibrant during pregnancy due to increased hormone levels. The story changes after giving birth. Nearly half of new mothers experience postpartum hair loss. Most hair shedding peaks between four to five months after delivery.
This hair loss, called telogen gravidarum, happens because estrogen levels drop after childbirth. The increased shedding might worry you, but note that this condition doesn’t last forever. Your hair should return to its normal fullness by your baby’s first birthday.
Menopause-Related Hair Thinning
Hair thickness and density often change as menopause approaches. Research shows that more than half of women deal with some form of menopause-related hair thinning. Declining estrogen and progesterone levels cause these changes by disrupting your hair’s growth cycle.
Menopause can bring:
- Overall hair thinning, especially at the crown
- Slower hair growth
- Changes in hair texture
- Thinning in other body areas
Hormonal changes during menopause can boost androgens, which may shrink your hair follicles. This process usually starts during perimenopause and continues through postmenopause. It affects both your scalp and other areas where hair grows.
Your hair’s growth cycle responds differently to thyroid health, pregnancy, and menopause stages. Understanding these relationships helps you take the right steps and get treatment when needed.
Stress-Related Hair Loss
New research shows a deep link between stress and hair loss. Your body’s stress response can directly affect how your hair grows. Scientists have found that stress hormones can force hair follicles to rest longer than they should.
Acute vs. Chronic Stress Effects
Your body reacts differently to short and long-term stress. A brief stressful period might temporarily mess with your hair cycle. Long-term stress leads to ongoing hair loss problems. Studies show that ongoing stress puts you at risk for health issues like depression, anxiety, and severe hair loss.
Long-term stress makes your body pump out more stress hormones, especially cortisol. These hormones can:
- Stop hair follicles from working normally
- Make the resting phase last longer
- Slow down new hair growth
- Cause inflammation around your follicles
Telogen Effluvium Explained
Telogen effluvium is the most common type of stress-related hair loss that affects your whole scalp. You might lose up to 300 hairs each day, which is way more than the normal 50-100 hairs.
You’ll start to notice more hair falling out about 2-4 months after something stressful happens. This happens because stress forces more of your hair into a “resting” phase. The actual hair loss comes months later as new growth pushes out the resting hairs.
There are two types of telogen effluvium:
- Acute: Lasts less than six months and usually starts after a specific event
- Chronic: Goes on for more than six months with no clear trigger
Stress Management Techniques
Your hair needs protection from stress-related loss. Here are some proven strategies that work:
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Eat a balanced diet full of proteins and vitamins
- Exercise regularly to keep stress in check
- Sleep 7-9 hours every night
Mental Health Support: Try stress-reduction methods like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga. Research shows that just a few minutes of daily meditation can help break the stress cycle that leads to hair loss.
Stress-related hair loss usually doesn’t last forever. Most cases of telogen effluvium go away within 6-8 months once you get your stress under control. If your hair keeps falling out or really bothers you, a healthcare provider can help you find the right treatment plan.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Your diet is a vital part of healthy hair growth, and lack of nutrients can affect your hair’s health by a lot. Studies show that micronutrients play major roles in the normal hair follicle cycle and affect cellular turnover in the follicle bulb.
Essential Vitamins for Hair Health
Several key vitamins help your hair grow:
Vitamin D: This nutrient helps create new hair follicles and boosts your immune system. Supplementation might help if you have hair loss with low vitamin D levels.
Vitamin C: This vitamin does more than boost general health. It has a vital role in:
- Helping your body absorb iron
- Supporting collagen production that strengthens hair
- Protecting hair follicles from oxidative stress
B-Complex Vitamins: Many companies market biotin (B7) for hair growth. Yet research shows that hair loss links only to deficiencies in riboflavin, biotin, folate, and vitamin B12.
Mineral Deficiencies and Hair Loss
Iron deficiency leads the list of nutritional deficiencies worldwide that cause hair loss. Women who experience hair loss should pay special attention to their iron levels:
- Women who menstruate face higher risks of iron deficiency
- Your serum ferritin levels need to stay above 40-70 ng/dL to prevent severe hair loss
Zinc levels can affect your hair health too. A study with over 300 people who had hair loss showed low zinc levels consistently. But it’s worth mentioning that too much of certain minerals, like zinc and selenium, can make hair loss worse.
Diet Recommendations for Healthy Hair
Your hair needs these nutrient-rich foods to stay healthy:
Protein Sources:
- Lean meats and poultry
- Fish, especially fatty fish rich in omega-3s
- Eggs and dairy products
Iron-Rich Foods:
- Dark leafy greens
- Lean red meat (85% lean or higher)
- Fortified cereals
Balance your daily calories this way:
- 20% from protein
- 20-30% from healthy fats
- 45-60% from carbohydrates
Sharp cuts in calories or carbs can make your hair thin and brittle. A balanced diet usually gives you all the nutrients you need. If blood tests show specific deficiencies, your doctor might suggest targeted supplements.
Medical Conditions Causing Hair Loss
Medical conditions can substantially affect your hair health. These range from autoimmune disorders to infections of all types. You should know these conditions to identify the right time to get professional medical help.
Autoimmune Disorders
Your immune system sometimes attacks your hair follicles by mistake and causes different types of hair loss. Alopecia areata, the most prominent autoimmune-related hair loss condition, affects nearly 7 million people in the United States. This condition can start at any age, and about 20% of cases occur in children.
Alopecia areata puts you at higher risk for other autoimmune conditions. People who have autoimmune diseases like psoriasis, thyroid disease, or vitiligo are more likely to develop this condition.
Your risk increases if you have:
- Asthma or hay fever
- Atopic dermatitis
- Close family members with autoimmune conditions
- Existing thyroid disorders
Scalp Infections and Diseases
Scalp infections lead to temporary or permanent hair loss based on their severity and treatment timing. A common scalp infection creates scaly and inflamed areas on your scalp that appear as small black dots – these are actually hair stubs.
Folliculitis decalvans stands out as a rare but serious scalp condition that causes ongoing inflammation of hair follicles. Round or oval-shaped bald spots appear and can lead to permanent hair loss with scarring.
Bacterial infections like Staphylococcus aureus are the most common hair problems. These can cause ongoing inflammation and destroy hair follicles without treatment. The good news is that most scalp infections respond well to treatment, and hair typically regrows after the infection clears.
Medication-Induced Hair Loss
Many medications can trigger hair loss as a side effect and disrupt your hair’s natural growth cycle. This type of hair loss usually shows up 2-4 months after starting a medication. Hair loss severity varies by medication type and your body’s sensitivity to it.
These medications often cause hair loss:
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Antidepressants, especially SSRIs, which can cause noticeable hair loss after about 8.6 weeks
- Blood pressure medications
- Arthritis treatments
- Acne medications containing vitamin A
Hair loss from medications is usually temporary. Hair starts growing back 3-6 months after stopping the medication. Your hair might take up to 18 months to look normal again.
Never stop taking your medication if you think it causes hair loss without talking to your healthcare provider first. They can adjust your dosage or switch you to a different medication that might be easier on your hair growth cycle.
Note that drug-induced hair loss can affect any part of your scalp or body. The severity depends on both the medication type and dosage. Your healthcare provider can run specific tests, including a hair pull test and scalp analysis, to find the exact cause and suggest the right treatment options.
Lifestyle Factors
Your daily choices and environment can make a huge difference to your hair’s health. We can’t control all causes of hair loss, but knowing how your lifestyle affects your hair helps prevent damage you can avoid.
Hairstyling Damage
You might be damaging your hair without even knowing it through your hairstyling habits. Up to one-third of women suffer from traction alopecia, a condition caused by tight hairstyles. This especially affects women of African descent. Your hair follicles face constant stress from tight ponytails, braids, or cornrows.
Tight styling can seriously damage your hair:
- Your first warning signs include scalp pain and small bumps
- You could face permanent scarring and irreversible hair loss if you don’t change your style
- The combination of extensions or weaves with relaxed hair creates the highest risk for traction alopecia
Heat styling damages your hair too. Your hair structure suffers major damage when you use tools above 347 degrees. This weakens your strands and leads to breakage, making your hair look thinner as time passes.
Environmental Impacts
Your hair battles various environmental factors daily that can lead to hair loss. Hair follicles become easy targets for environmental pollutants because of their high levels of proliferation and perfusion.
Key Environmental Stressors:
- Exposure to particulate matter (PM) triggers inflammatory responses and links to alopecia areata
- UV radiation creates oxidative damage and disrupts hair follicle function
- Tobacco smoke harms hair through multiple pathways, including vasoconstriction and increased cellular senescence
Billions of pollution particles can settle on your hair surface in heavily polluted areas, which changes its structure and removes its shine. People living in urban, industrialized areas lose more hair than those in rural regions.
Daily Habits Affecting Hair Health
Your routines can either protect or harm your hair health. Research shows several lifestyle factors that lead to hair loss:
-
Diet and Exercise Habits:
- Hair growth suffers from very low-calorie diets
- You might lose hair if you completely avoid alcohol and exercise too much
-
Sleep and Stress Management:
- Bad sleep quality puts your hair at risk
- You might lose more hair if you drink too much caffeine
Product Usage Impact: More products don’t always mean better hair care. Too much shampooing makes your scalp produce extra oils, which might increase hair fall. Styling products with alcohol can make your hair break easily during brushing.
These evidence-based practices can protect your hair:
- Switch up your hair partition and styles often to avoid constant tension
- Pick soft, non-static scrunchies made with cotton fibers or pure silk
- Don’t rub wet hair vigorously with a towel
- Cut down on heat treatments and always protect your hair from heat
Small habits add up to affect your hair health. Research links smoking, drinking more than four alcoholic drinks weekly, and longer stress periods to hair loss. You can keep your hair healthy and prevent unnecessary loss by making smart choices about your daily hair care routine and lifestyle habits.
Best selling hair growth products:
Prevention and Treatment Options
You can fight hair loss by learning about your treatment options. Many proven solutions can help manage and even reverse hair loss, whether you notice early thinning or experience a lot of loss.
Early Intervention Strategies
Quick action is crucial to treat hair loss successfully. Studies show that treating hair loss in its early stages will boost your chances to maintain and regrow hair. Your hair follicles respond better to medications and therapies if you start treatment early.
These proven early intervention approaches work well:
- Talk to a hair loss specialist to get the right diagnosis
- Begin FDA-approved treatments at first signs of loss
- Take care of underlying health conditions
- Change harmful hair care habits
A typical hair transplant moves patches of hair from your head and places each follicle into bald areas. Starting treatment early gives you more donor hairs available for transplantation.
Medical Treatments Available
Hair loss treatments vary in approach, effectiveness, and side effects. Below is a comprehensive comparison of popular options, including the innovative Hairegen devices, which stand out for their safety, convenience, and proven effectiveness.
Treatment Comparison Table
| Treatment Type | Application | Expected Timeline | Side Effects | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil (Rogaine®) | Topical | 6–12 months | Scalp irritation, initial shedding, potential hair loss reversal upon stopping | Men & Women |
| Finasteride (Propecia®) | Oral | 3–6 months | Reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, hormonal imbalance (men only) | Men Only |
| Hair Transplant Surgery | Surgical | 6–12 months | Scarring, swelling, infection, long recovery time | Advanced Hair Loss |
| PRP Therapy | Injectable | 3–6 months | Mild swelling, redness, discomfort at injection sites | Both Genders |
| Hairegen Classic/Premium | Device (Topical + Advanced Tech) | 3–4 months | Clinically proven safe, no significant side effects reported | Men & Women (All Stages) |
Advanced Treatment Options
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- Involves injecting your own plasma to stimulate growth.
- Helps slow loss and encourages new hair growth.
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
- FDA-approved for hereditary hair loss.
- Non-invasive and effective for both men and women.
-
Hair Transplant Surgery:
- Surgical option for permanent restoration.
- Suitable for advanced hair loss cases.
-
Hairegen Devices (Classic & Premium):
- Non-invasive home treatment that uses electrical, biochemical, and mechanical stimulation.
- Designed to stop hair loss, reactivate dormant follicles, and promote natural regrowth.
- Proven results in 92% of users with visible improvements in just 3–4 months.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
While medical treatments often yield the best results, natural remedies can complement them:
-
Essential Nutrients:
- Iron: Supports deficiency-related hair loss.
- Vitamin D: Improves follicular health.
- Zinc: Enhances overall hair strength and vitality.
-
Scalp Care Techniques:
- Regular scalp massages improve blood flow to follicles.
- Essential oils, like rosemary, stimulate circulation.
- Gentle hair care routines prevent further damage.
Combining Treatments for Better Results
- Studies show that combining treatments, such as topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, produces better outcomes than using a single method.
- Adding Hairegen to your treatment plan can further enhance results by stimulating the scalp through advanced technology, complementing other therapies.
Important Considerations
Success with hair loss treatments depends on factors such as:
- The underlying cause and pattern of hair loss.
- Your age, gender, and overall health.
- Consistency and long-term commitment to treatment.
- Budget and willingness to integrate multiple solutions.
Why Choose Hairegen?
Hairegen provides an innovative, drug-free solution for men and women battling hair loss. Its unique combination of mechanical, electrical, and biochemical actions makes it a standout option in both early and advanced stages of hair loss. Work with your healthcare provider to incorporate Hairegen into your treatment plan and achieve the best possible outcomes.