The fitness world is abuzz with discussions about creatine, a popular supplement known for its potential to enhance athletic performance and muscle growth. However, amidst the praise, a lingering concern has emerged: does creatine cause hair loss? This question has sparked debates among fitness enthusiasts, researchers, and medical professionals alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the science behind creatine, examine its purported link to hair loss, and provide you with evidence-based insights to help you make informed decisions about your supplement regimen and hair health.

Understanding Creatine: Nature’s Energy Booster
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small quantities in certain foods and synthesized by the human body. It plays a crucial role in energy production, particularly during high-intensity, short-duration activities like weightlifting or sprinting.
The Science Behind Creatine’s Function
At its core, creatine works by increasing the availability of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. By enhancing ATP production, creatine allows muscles to perform more work before fatigue sets in, potentially leading to improved strength and muscle gains.
Dietary Sources and Supplementation
While creatine is present in foods like red meat and fish, the amounts are relatively small. This is why many athletes and fitness enthusiasts turn to creatine supplements to boost their intake and maximize potential benefits.
The Hair Loss Conundrum: Examining the Claims
The Origin of the Creatine-Hair Loss Connection
The notion that creatine might cause hair loss stems primarily from a 2009 study involving rugby players. This research suggested a potential link between creatine supplementation and increased levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone associated with male pattern baldness.
Analyzing the Evidence: What Do Studies Really Show?
While the 2009 study raised eyebrows, it’s crucial to note that subsequent research has failed to replicate these findings. Multiple studies examining creatine’s effects on hormone levels, including DHT, have not found significant changes that would likely contribute to hair loss.
The Role of DHT in Hair Loss
To understand the potential connection, it’s essential to explore how DHT affects hair follicles. This hormone can bind to receptors in susceptible hair follicles, potentially leading to miniaturization and eventual hair loss in genetically predisposed individuals.
Creatine’s Impact on Hormones: A Closer Look
Testosterone and DHT: The Hormonal Interplay
Creatine’s alleged effect on hair loss centers around its potential influence on testosterone and DHT levels. However, the scientific consensus suggests that creatine’s impact on these hormones, if any, is minimal and unlikely to significantly affect hair growth patterns.
Debunking Myths: Creatine and Testosterone Conversion
Contrary to popular belief, there’s little evidence to support the idea that creatine directly increases the conversion of testosterone to DHT. The body’s hormonal regulation is complex, and creatine supplementation doesn’t appear to disrupt this delicate balance in ways that would promote hair loss.
Individual Variability: Why Responses May Differ
It’s important to recognize that individuals may respond differently to creatine supplementation. Factors such as genetics, overall health, and existing hormone levels can influence how one’s body processes and utilizes creatine.
The Benefits of Creatine: Beyond Muscle Growth
Enhanced Athletic Performance
Creatine’s primary claim to fame is its ability to improve athletic performance, particularly in high-intensity, short-duration activities. Users often report increased strength, power, and muscle endurance.
Cognitive Function and Brain Health
Emerging research suggests that creatine may have benefits beyond physical performance. Some studies indicate potential cognitive enhancements and neuroprotective effects, particularly in older adults or those with certain neurological conditions.
Muscle Recovery and Injury Prevention
Creatine’s role in energy production may also contribute to faster muscle recovery and reduced risk of injury, making it a valuable tool for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike.
Treatment Approaches for Trichotillomania: Therapeutic Interventions
Effective treatment for trichotillomania often involves a combination of therapeutic interventions tailored to the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, several evidence-based treatments have shown promise in helping individuals manage their hair-pulling urges and improve their overall quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a widely used and effective treatment for trichotillomania. This approach focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with hair-pulling. Key components of CBT for trichotillomania include:
- Psychoeducation about the disorder
- Self-monitoring of hair-pulling behaviors
- Identifying triggers and high-risk situations
- Developing alternative coping strategies
- Challenging and reframing negative thoughts
- Gradual exposure to triggering situations
- Relapse prevention planning
Habit Reversal Training (HRT)
Habit Reversal Training is a specific type of behavioral therapy that has shown significant success in treating trichotillomania. The main components of HRT include:
- Awareness training: Helping individuals recognize the urge to pull hair and the situations that trigger it
- Competing response training: Teaching alternative behaviors to replace hair-pulling, such as clenching fists or engaging in a different activity
- Social support: Involving family members or friends in the treatment process to provide encouragement and reinforcement
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy is an approach that combines mindfulness techniques with behavioral strategies. ACT for trichotillomania focuses on:
- Accepting the presence of hair-pulling urges without judgment
- Developing psychological flexibility
- Clarifying personal values and goals
- Committing to actions that align with those values
- Mindfulness practices to increase present-moment awareness
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavior Therapy, originally developed for treating borderline personality disorder, has shown promise in addressing trichotillomania. DBT skills that can be particularly helpful include:
- Mindfulness techniques
- Distress tolerance skills
- Emotion regulation strategies
- Interpersonal effectiveness training
Group Therapy
Participating in group therapy sessions can provide valuable support and opportunities for shared learning among individuals with trichotillomania. Benefits of group therapy include:
- Reduced feelings of isolation and shame
- Sharing of coping strategies and experiences
- Mutual support and encouragement
- Opportunities for role-playing and skill practice
Family Therapy
Involving family members in the treatment process can be beneficial, especially for children and adolescents with trichotillomania. Family therapy can focus on:
- Educating family members about the disorder
- Improving communication and support within the family
- Addressing family dynamics that may contribute to hair-pulling behaviors
- Developing strategies for supporting the individual’s recovery
Hypnotherapy
Some individuals with trichotillomania have reported benefits from hypnotherapy, although more research is needed to establish its effectiveness. Hypnotherapy may be used to:
- Reduce stress and anxiety
- Enhance relaxation and self-control
- Reinforce positive behaviors and coping strategies
It is important to note that the effectiveness of these therapeutic interventions can vary from person to person. Working closely with a mental health professional experienced in treating trichotillomania can help individuals determine the most appropriate treatment approach for their specific needs and circumstances.
Medication Options for Managing Trichotillomania
While psychotherapy is often the primary treatment for trichotillomania, medication can play a supportive role in managing symptoms for some individuals. It’s important to note that no medication has been specifically approved by regulatory agencies for the treatment of trichotillomania. However, several types of medications have shown promise in clinical studies and may be prescribed off-label by healthcare providers.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are a class of antidepressants that are sometimes used to treat trichotillomania. These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which may help reduce hair-pulling urges and associated anxiety. Examples of SSRIs that have been studied for trichotillomania include:
- Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro)
While some individuals report benefits from SSRIs, research results have been mixed, and more studies are needed to establish their effectiveness for trichotillomania.
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)
N-Acetylcysteine is an amino acid supplement that has shown promise in treating trichotillomania. NAC is thought to work by regulating glutamate, a neurotransmitter involved in compulsive behaviors. Some studies have found that NAC can help reduce hair-pulling urges and improve overall symptoms. Benefits of NAC include:
- Generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects
- Available over-the-counter as a dietary supplement
- May be used alone or in combination with other treatments
Antipsychotic Medications
In some cases, low doses of antipsychotic medications may be prescribed to help manage trichotillomania symptoms. These medications work by affecting dopamine levels in the brain and may help reduce impulsive behaviors. Examples include:
- Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
- Aripiprazole (Abilify)
- Risperidone (Risperdal)
It’s important to note that antipsychotic medications can have significant side effects and should be used with caution under close medical supervision.
Naltrexone
Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist that has been studied for its potential in treating trichotillomania. While primarily used for alcohol and opioid dependence, some research suggests it may help reduce hair-pulling urges in some individuals. However, more studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness.
Clomipramine
Clomipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant that has shown some efficacy in treating trichotillomania. It works by affecting both serotonin and norepinephrine levels in the brain. While it may be effective for some individuals, it can have more side effects compared to newer antidepressants.
Considerations for Medication Use
When considering medication for trichotillomania, it’s important to keep the following points in mind:
- Medications are typically used in conjunction with psychotherapy, not as a standalone treatment
- Response to medication can vary greatly between individuals
- It may take several weeks to notice improvements in symptoms
- Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor effectiveness and side effects
- Abruptly stopping medication can lead to withdrawal symptoms or a return of trichotillomania symptoms
It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider experienced in treating trichotillomania to determine the most appropriate medication regimen. They can help weigh the potential benefits against possible side effects and monitor progress over time.
Coping Strategies and Self-Help Techniques for Trichotillomania
While professional treatment is often necessary for managing trichotillomania, there are numerous self-help strategies and coping techniques that individuals can employ to support their recovery and reduce hair-pulling urges. These techniques can be used in conjunction with therapy and medication to enhance overall treatment effectiveness.
Identifying Triggers and Patterns
One of the first steps in managing trichotillomania is to become more aware of personal triggers and hair-pulling patterns. This can be achieved through:
- Keeping a hair-pulling diary to track when, where, and why urges occur
- Noting emotional states or situations that precede hair-pulling episodes
- Identifying specific sensations or textures that trigger the urge to pull
By understanding these patterns, individuals can develop targeted strategies to address their unique triggers.
Stimulus Control Techniques
Stimulus control involves modifying the environment to reduce opportunities for hair-pulling. Some effective strategies include:
- Wearing gloves or bandages on fingers to create a physical barrier
- Covering mirrors or avoiding well-lit areas that make it easier to see and pull hair
- Changing hairstyles or using accessories to make hair less accessible
- Removing tweezers or other tools that may be used for pulling
Habit Reversal Strategies
Implementing habit reversal techniques can help interrupt the hair-pulling cycle. Some useful strategies include:
- Engaging in a competing response, such as clenching fists or pressing fingertips together when the urge to pull arises
- Using fidget toys or stress balls to keep hands occupied
- Practicing deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation to manage tension
- Redirecting the urge by gently stroking or massaging the affected area instead of pulling
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation practices into daily routines can help reduce stress and increase awareness of hair-pulling urges. Useful techniques include:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Guided imagery
- Deep breathing exercises
- Yoga or tai chi
Regular practice of these techniques can help individuals become more attuned to their thoughts and emotions, making it easier to recognize and manage hair-pulling urges.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining overall physical and mental well-being can support efforts to manage trichotillomania. Important lifestyle factors to consider include:
- Regular exercise to reduce stress and improve mood
- Adequate sleep to promote emotional regulation
- Balanced nutrition to support brain health
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, which can exacerbate anxiety and impulsivity
- Engaging in enjoyable hobbies and activities to reduce boredom and stress
Support Networks
Building a strong support network is crucial for individuals managing trichotillomania. This can include:
- Joining support groups or online communities for people with trichotillomania
- Confiding in trusted friends or family members about the condition
- Working with a therapist or counselor who specializes in trichotillomania
- Connecting with advocacy organizations that provide resources and support
Self-Compassion and Acceptance
Developing self-compassion and acceptance is an important aspect of coping with trichotillomania. This involves:
- Recognizing that setbacks are a normal part of the recovery process
- Practicing self-forgiveness when hair-pulling episodes occur
- Challenging negative self-talk and replacing it with more compassionate thoughts
- Focusing on progress and small victories rather than perfection
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find benefit in exploring alternative or complementary therapies to support their trichotillomania management. These may include:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Art therapy
- Music therapy
- Aromatherapy
While the effectiveness of these approaches may vary, they can provide additional tools for stress reduction and self-expression.
By incorporating a combination of these self-help strategies and coping techniques into their daily lives, individuals with trichotillomania can enhance their ability to manage hair-pulling urges and support their overall recovery process. It’s important to remember that finding the most effective combination of strategies may take time and experimentation, and what works for one person may not work for another. Patience, persistence, and self-compassion are key elements in developing a successful self-help approach to managing trichotillomania.
Best selling hair growth products:
Potential Side Effects of Creatine Use
Water Retention and Weight Gain
One of the most commonly reported side effects of creatine supplementation is initial weight gain due to increased water retention in muscles. This effect is typically temporary and not associated with fat gain.
Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Some users may experience mild digestive issues when starting creatine supplementation. These symptoms often subside as the body adjusts to the supplement.
Kidney and Liver Concerns: Separating Myth from Reality
While concerns have been raised about creatine’s impact on kidney and liver function, extensive research has shown that creatine is safe for healthy individuals when used as directed. However, those with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions should consult a healthcare provider before use.
Safe Usage Guidelines: Maximizing Benefits, Minimizing Risks
Recommended Dosage and Timing
The most common and well-studied form of creatine is creatine monohydrate. A typical dosage involves a loading phase of 20 grams per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams daily.
Cycling Creatine: Necessary or Not?
While some advocate for cycling creatine use, current research suggests that continuous use is safe and effective for most individuals. The body’s natural creatine production doesn’t appear to be negatively affected by long-term supplementation.
Combining Creatine with Other Supplements
Creatine can be safely combined with other common supplements like protein powders and multivitamins. However, it’s always wise to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Hair Loss: Understanding the Real Culprits
Genetic Factors: The Primary Driver of Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness, the most common form of hair loss, is primarily driven by genetic factors. The presence of certain genes can make hair follicles more susceptible to the effects of DHT.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
While genetics play a significant role, factors such as stress, poor nutrition, and certain hairstyling practices can contribute to hair loss or exacerbate existing conditions.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Various medical conditions and medications can lead to hair loss. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing unexpected hair thinning or loss.
Addressing Hair Loss: Effective Strategies and Treatments
FDA-Approved Medications
Medications like minoxidil and finasteride have shown effectiveness in treating hair loss for many individuals. These treatments work by promoting hair growth or blocking DHT’s effects on hair follicles.
Emerging Therapies: PRP and Low-Level Laser Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments and low-level laser therapy are gaining popularity as potential hair loss solutions. While more research is needed, early results are promising for some individuals.
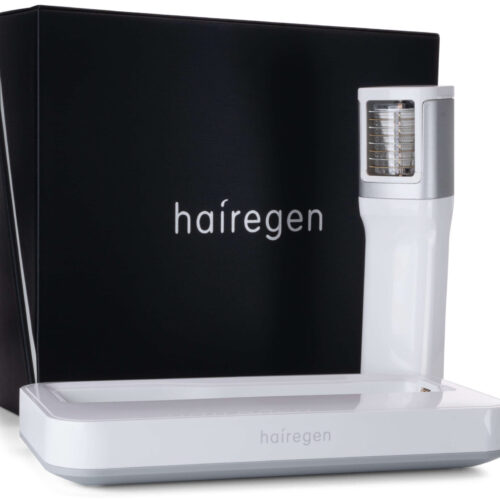
The Hairegen Device: A New Frontier in Hair Loss Treatment
The Hairegen device represents an innovative approach to combating hair loss. This at-home treatment utilizes low-level laser therapy to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth. While relatively new, early user reports and studies suggest it may be a promising option for those seeking non-invasive hair loss solutions.
Making Informed Decisions: Balancing Goals and Concerns
Assessing Your Personal Risk Factors
When considering creatine supplementation, it’s essential to evaluate your personal risk factors for hair loss, including family history and current hair health.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
Before starting any new supplement regimen, particularly if you have concerns about hair loss, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare provider or dermatologist who can offer personalized advice.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Approach
If you choose to use creatine, pay attention to any changes in your hair or overall health. Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider can help you track any potential effects and adjust your approach as needed.
The Future of Creatine Research and Hair Health
Ongoing Studies and Emerging Insights
The scientific community continues to investigate creatine’s effects on various aspects of health, including its potential impact on hair. Staying informed about new research can help you make the best decisions for your health and fitness goals.
Personalized Approaches to Supplementation
As our understanding of genetics and individual responses to supplements grows, we may see more personalized approaches to creatine use and hair loss prevention in the future.
Integrating Holistic Health Practices
Ultimately, maintaining healthy hair involves a holistic approach that includes proper nutrition, stress management, and overall wellness practices. Integrating these elements with informed supplement use can help you achieve your fitness goals while supporting hair health.
In conclusion, while concerns about creatine causing hair loss persist, the current body of evidence does not support a direct causal link. Creatine remains a popular and generally safe supplement for enhancing athletic performance and muscle growth. However, individuals concerned about hair loss should approach any supplement regimen with caution, consult healthcare professionals, and consider their personal risk factors. By staying informed and taking a balanced approach, you can make the best decisions for your fitness journey and overall health, including the health of your hair.